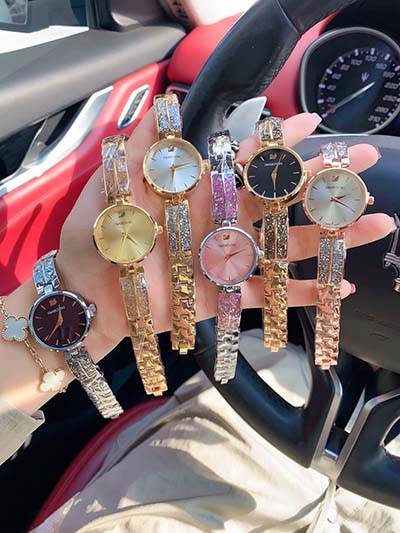
lv impella | distal part of Impella lv impella We hypothesized that mechanical LV unloading with the Impella will safely decrease LV wall stress and increase coronary flow and microvascular perfusion (MP) within the infarct, peri‐infarct, and remote regions in a porcine .
The Vintage Rolex Datejust 1600, introduced in the 1960s, represents a pivotal era for Rolex, characterized by innovations in both design and technology. As .
0 · morphology of Impella management
1 · distal part of Impella
2 · Impella system for cardiac intensivist
3 · Impella pump catheter
4 · Impella management procedure
5 · Impella left ventricular
6 · Impella indications
7 · Impella catheter for cardiac intensivist
Shop The Collection. The Purist’s Vintage Rolex: Air-King 5500. Although it receives far less attention than the Submariner, Day-Date, or GMT-Master, the Rolex Air-King is .
In this context, Impella settings may be titrated primarily to achieve LV .
The Impella mechanical circulatory support (MCS) system is a catheter-based continuous flow . Jo Kajewski, an Abiomed advanced Impella trainer, describes how the left .Impella unloads the left ventricle percutaneously and contributes to cardiac recovery. •. Impella improves pulmonary congestion and systemic perfusion. •. Indications of Impella range as follows: ST-elevation myocardial infarction, .
In this study, we conducted 2 modes of LV support using Impella: partial (p-Impella) and total (t-Impella) support. p-Impella is partial LV support, .
We hypothesized that mechanical LV unloading with the Impella will safely decrease LV wall stress and increase coronary flow and microvascular perfusion (MP) within the infarct, peri‐infarct, and remote regions in a porcine .A culprit oriented approach should be used when troubleshooting the Impella supported patient .Impella Left Ventricular (LV) Support Systems (Impella 2.5, Impella CP, Impella CP with .

Impella is an axial flow left ventricular assist device (LVAD) built into the tip of a catheter. It is inserted via a peripheral artery and implanted into the left ventricle. In this context, Impella settings may be titrated primarily to achieve LV decompression (rather than against systemic cardiac output, which is largely provided by the ECMO circuit). ECMO is often weaned off first, with Impella subsequently weaned off.
The Impella mechanical circulatory support (MCS) system is a catheter-based continuous flow cardiac assist device that is widely used in the treatment of cardiogenic shock in medical and surgical cardiac intensive care units.
Jo Kajewski, an Abiomed advanced Impella trainer, describes how the left ventricular (LV) waveform is derived and how left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) is measured from that waveform with the Impella with SmartAssist technology.Impella unloads the left ventricle percutaneously and contributes to cardiac recovery. •. Impella improves pulmonary congestion and systemic perfusion. •. Indications of Impella range as follows: ST-elevation myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, fulminant myocarditis. •. In this study, we conducted 2 modes of LV support using Impella: partial (p-Impella) and total (t-Impella) support. p-Impella is partial LV support, in which the LV remains ejecting. In p-Impella, we adjusted the Impella flow to halve the AP pulse pressure. We hypothesized that mechanical LV unloading with the Impella will safely decrease LV wall stress and increase coronary flow and microvascular perfusion (MP) within the infarct, peri‐infarct, and remote regions in a porcine model of ischemic HF.
A culprit oriented approach should be used when troubleshooting the Impella supported patient with signs of persistent circulatory failure. Right ventricular failure is an important cause of insufficient preload during left ventricular Impella support. The Impella can dislodge during cardiopulmonary resuscitation and position
morphology of Impella management
Impella Left Ventricular (LV) Support Systems (Impella 2.5, Impella CP, Impella CP with SmartAssist, Impella 5.0, and Impella 5.5 with SmartAssist) are authorized for emergency use by HCPs in the hospital setting for providing temporary (≤ 4 days for Impella 2.5, Impella CP, and Impella CP with SmartAssist; and ≤ 14 days for Impella 5.0 and .
Impella is an axial flow left ventricular assist device (LVAD) built into the tip of a catheter. It is inserted via a peripheral artery and implanted into the left ventricle. The Impella LV Support Systems are a temporary left heart pump intended to help you maintain stable heart function without open chest surgery. It includes a mini heart pump mounted at the end. In this context, Impella settings may be titrated primarily to achieve LV decompression (rather than against systemic cardiac output, which is largely provided by the ECMO circuit). ECMO is often weaned off first, with Impella subsequently weaned off.
The Impella mechanical circulatory support (MCS) system is a catheter-based continuous flow cardiac assist device that is widely used in the treatment of cardiogenic shock in medical and surgical cardiac intensive care units.
Jo Kajewski, an Abiomed advanced Impella trainer, describes how the left ventricular (LV) waveform is derived and how left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) is measured from that waveform with the Impella with SmartAssist technology.Impella unloads the left ventricle percutaneously and contributes to cardiac recovery. •. Impella improves pulmonary congestion and systemic perfusion. •. Indications of Impella range as follows: ST-elevation myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy, fulminant myocarditis. •. In this study, we conducted 2 modes of LV support using Impella: partial (p-Impella) and total (t-Impella) support. p-Impella is partial LV support, in which the LV remains ejecting. In p-Impella, we adjusted the Impella flow to halve the AP pulse pressure. We hypothesized that mechanical LV unloading with the Impella will safely decrease LV wall stress and increase coronary flow and microvascular perfusion (MP) within the infarct, peri‐infarct, and remote regions in a porcine model of ischemic HF.
A culprit oriented approach should be used when troubleshooting the Impella supported patient with signs of persistent circulatory failure. Right ventricular failure is an important cause of insufficient preload during left ventricular Impella support. The Impella can dislodge during cardiopulmonary resuscitation and positionImpella Left Ventricular (LV) Support Systems (Impella 2.5, Impella CP, Impella CP with SmartAssist, Impella 5.0, and Impella 5.5 with SmartAssist) are authorized for emergency use by HCPs in the hospital setting for providing temporary (≤ 4 days for Impella 2.5, Impella CP, and Impella CP with SmartAssist; and ≤ 14 days for Impella 5.0 and .Impella is an axial flow left ventricular assist device (LVAD) built into the tip of a catheter. It is inserted via a peripheral artery and implanted into the left ventricle.
distal part of Impella
On July 21, 1969, Buzz Aldrin was wearing an Omega Speedmaster wristwatch when he became the second man to walk on the moon. To get there, the .
lv impella|distal part of Impella